Wireless Power Transfer: The Future of Energy Transmission
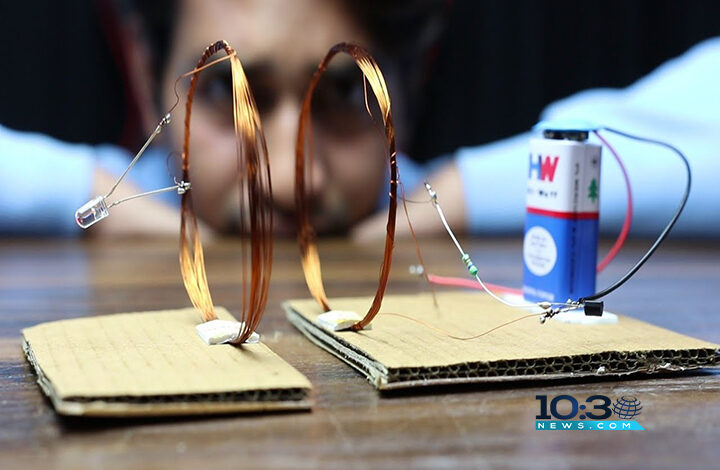
Wireless Power Transfer
The technology of wireless power transfer is not just an idea from visionary fiction but a fast-developing means that changes the way we think about energy transfer.
Imagine a world where, if all attempts were unsuccessful, they led to the roots that show us developments today.
Now, as mobile devices, electrical vehicles, and other portable technologies come into being, the demand for an electronic device that charges itself with no plug has risen. This is the promise of wireless power transfer.
This is such revolutionary technology that will allow electricity to be transmitted from the source of power into a device without a physical connector, like cables or wires.
The idea of transferring power wirelessly is not new. Nikola Tesla developed an interest in the area of wireless power transfer in the early 20th century. Though his early search for efficient wireless power solutions has never been greater.
How WPT Works
At its very core, wireless power transfer is nothing more than energy transfer without direct electrical contact.
But how exactly is this supposed to work? The fundamental principle involves creating a magnetic field that can convey energy between points.
This has most often been actualized through the use of electromagnetic waves, which are capable of moving through air in almost the same way as radio waves can carry sound.
Several key enabling technologies make possible the transmission of electric power without wires. These include inductive coupling, capacitive coupling, resonant inductive coupling, magnetodynamic coupling, power transfer by microwave means, and laser power transfer.
Here we have some ways that represent much different effectiveness, distance, and application.
Types of wireless power transfer
There are many different forms of wireless energy transfer. Each format to suit different uses and needs.
Inductive coupling
This is the most common form of inductively coupled WPF. This is especially true in consumer electronics. The technology works by creating a magnetic field between two coils. One in the source and the other in the device.
Usage of inductive pairing: This is a common method used in smartphone charging pads. smart watch and other small electronic devices This is a simple and effective method. But it must be close to the charger and the device.
Inductive Resonance Coupling
This allows for more distance between the power source and the device with a resonant inductive connection. This is another step in connecting the inputs by tuning the source and receiver to the same resonant frequency. To increase transfer efficiency over a longer period
Real-world example: This technology is being explored for wireless electric vehicle (EV) charging, where cars can be charged by simply parking on a charging pad. Without using a plugin…
Capacitive coupling
Another is capacitive coupling. where it passes through an electric field, not a magnetic field This technology uses conductive plates to create a capacitive connection between the power source and the device.
Used in Modern Devices: Capacitive connections are used in some wireless charging solutions for small devices. Although less common than inductive connections due to limitations in energy transfer efficiency…
magnetic coupling
magnetic coupling
Application of WPT
Wireless power transfer is used in many different industries, revolutionizing the way devices and systems are powered.
Electrical appliance
Wireless power transfer is the definition of convenience in the world of appliances. Everything from smartphones to smartwatches must be charged wirelessly. It will take us away from the cable problem.
Smartphones and Wearables: Inductive pairing is what the latest iPhones, Android phones, and other wearables like the Apple Watch now use for wireless charging. This makes it easier for users to ensure their devices are always on.
Wireless Charging Pads: These charging pads are commonly found in homes, cars, and public places. Allows for quick and easy charging without having to plug in.
automotive industry
The automotive industry is one of the most exciting areas for wireless energy transfer. Especially with the rise of electric vehicles (EV).
Wireless EV Charging: Imagine you are moving in and transforming your garage. Your car starts charging without interruption when you plug it in. That’s the future of wireless EV charging, and it will come in the form of resonance inductive coupling technology.
Future trends: As wireless charging technology improves We will see charging pads buried along the road. This makes it possible to charge EVs and becomes a game changer for the automotive industry.
Health care
In healthcare, WPF makes medical devices more accessible and non-invasive.
Medical implants: Devices such as pacemakers and cochlear implants can be driven wirelessly. This eliminates the need for surgery to replace batteries.
Portable Medical Devices: Wireless charging is also used for portable medical devices. This makes it more convenient for patients who need to use it while traveling.
Minimizing the size of cables and connectors
As we move towards a wireless future Reducing the number of cables and connectors is a big step forward.
Stepping into a Wireless Future: Less Clutter Fewer connectors and a cleaner, more flexible environment. These are just some of the benefits of adopting wireless power transfer…
Safety and durability
Wireless power transfer can improve safety and durability.
Reduced wear and tear: When there are no physical connectors to wear out. Electrical appliances will last longer. And the risk of electric shock is reduced.
Problems and limitations
Although there are many advantages But wireless energy transfer still faces many challenges that need to be solved.
Energy efficiency
One of the main challenges is energy efficiency. Today’s wireless power systems are less efficient than wired connections. Power loss occurs during transmission.
Current Performance Rate: Although efforts are being made to improve performance, But it is still a major obstacle.
Optimization efforts: Researchers are looking for new materials and techniques. to improve efficiency but is still in progress
Category limits
Another limitation is the range over which energy is transferred.
Range Challenge: Most wireless power systems have limited range. This may prevent widespread use.
Possible solution: Innovations in resonance-magnetodynamic coupling will expand the scope of operations. But more work is needed.
Spending factor
Cost is another factor to consider. Especially in the areas of production and implementation.
Construction and operating costs: Building and installing a wireless electrical system can be expensive. This may hinder wider adoption.
FAQs
- What is the most efficient type of wireless power transfer?
- Currently, resonant inductive coupling is considered one of the most efficient types, especially for applications like EV charging.
- Can wireless power transfer work over long distances?
- While traditional methods like inductive coupling have a limited range, microwave and laser-based power transfer can work over longer distances, though with some trade-offs in efficiency and safety.
- Is wireless power transfer safe for humans?
- Yes, when used within regulated limits, wireless power transfer is generally safe. However, ongoing research is needed to ensure safety over long-term exposure.
- What industries will benefit most from wireless power transfer?
- Consumer electronics, automotive, healthcare, and industrial sectors are likely to see the most significant benefits from wireless power transfer.
- How does wireless power transfer affect battery life?
- Wireless power transfer doesn’t inherently harm battery life, but like any charging method, the design and usage patterns can impact how long a battery lasts.
Regulatory and Safety Concerns
Finally, regulatory and safety concerns need to be addressed.
- Government Regulations: Governments are beginning to implement wireless power transfer, particularly in terms of safety and interference with other devices.
- Addressing Health Risks: There are concerns about the potential health risks associated with prolonged exposure to electromagnetic fields, and these need to be carefully managed.
Future of WPT
The future of WPF is bright, with several exciting developments on the horizon.
Emerging Technologies
As technology continues to evolve, new methods of WPF are emerging.
Innovations on the Horizon: From improved efficiency to longer range and lower costs, the future of wireless power transfer is full of potential.
Potential Impact on Society
Wireless power transfer has the potential to revolutionize how we live and work.
Changing the Face of Power Distribution: Wireless power is going to redefine how we distribute and use energy as it finds its way to full commercialization—into a more connected, more efficient world.
Conclusion
It’s way more than the convenience of charging devices wirelessly; the technology will change life and work. Its benefits outweigh the challenges to its realization, and it has a bright future ahead.
The further we press into innovation and improvement, the greater and more integral wireless power transfer will be in our daily lives, continuing to leverage us closer to a truly wireless and connected future.